

The turbulence constant, F B, must be obtained before this graph can be prepared. The permeability thickness product would then be a function of the slope of the resulting line. 2, consisting of two variables, bottom-hole flowing pressure, Pwf, and gas production rate qr, both measured pressure, Pwf, and gas production rate qr, both measured during the test, be plotted against the logarithm of test time, t. They propose that the entire group on the left side of Eq. They propose, however, that for a test with flow rate varying slightly, the test is modeled adequately by a simple rearrangement of Eq. Winestock and Colpitts point out that use of the equation in this form can lead to serious errors if it is applied to analyze drawdown tests in which flow rates vary even slightly during the test. The fundamental assumptions of the GRF model are 1) flow is radial, occurring within a homogeneous and isotropic medium from a single source, and fills an n-dimensional space 2) flow obeys Darcys. Winestock Pwf, and test time, t, are assumed to be constant.

In this equation all terms except flowing bottom-hole pressure, Pwf, and test time, t, are assumed to be constant. A frequently used equation describing a pressure drawdown test in a gas well is pressure drawdown test in a gas well is+F (1) The purpose of our investigations, therefore, was to find the limits of applicability of the Winestock and Colpitts method.įirst, we reviewed their proposed method and the reason for the method. This claim requires justification because the method proposed by Winestock and Colpitts is an approximation, and it clearly must fail when the rate of change in flow rate is sufficiently large. 0:00 / 52:48 Webinar: Conducting Pumping Tests and Improving Results In-Situ 1.05K subscribers 30K views 9 years ago Water Monitoring Webinars This webinar discusses step-drawdown and. In fact, Winestock and Colpitts claimed that the method they proposed would be adequate in general for smoothly varying flow rates, even though the total change in flow rate from beginning to end of a test was large.
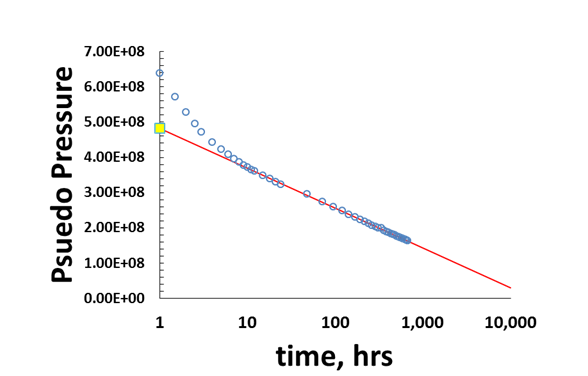
Winestock and Colpitts showed that both problems could be avoided if gas-well drawdown tests were run with a fixed choke - usually resulting in a slowly decreasing flow rate during the test - if a simple modification of conventional analysis theory is employed. Typically, aquifer properties are estimated from a constant-rate pumping test by fitting mathematical models to drawdown data through a procedure known as curve matching. The constant flow rate is maintained, but only with a great deal of difficulty. The constant flow rate requirement is frequently ignored, and use of conventional analysis on such tests has led to serious error in many cases, leading to a loss of confidence in drawdown testing or In practice, however, the theoretical requirement that flow rates must be maintained strictly constant during the test has led to two major problems: The information is used mainly for developing the final design of the pump facility and water delivery system. Ground Water, 40(5): 465.Use of pressure drawdown tests to characterize gas wells has long been accepted, in principle, to be an excellent formation evaluation technique. The purpose of a pump test is to obtain information on well yield, observed drawdown, pump efficiency, and calculated specific capacity. The hydro-malaprop and the ground water table. Geological Survey Water Supply Paper, 887. Methods of determining permeability of water bearing materials with special references to discharging well methods. The relation between the lowering of the piezometric surface and the rate and duration of discharge of a well using groundwater storage. Aquifer Test Design Observation and Data Analysis: Techniques of Water-Resource Investigation.
#DRAWDOWN TEST PROCEDURE PROFESSIONAL#
Geological Survey Professional Paper 708. Publication 47, International Institute for Land Reclamation and Improvement, P.O. In this textbook, the most important methods of well tests and their evaluations are. Analysis and Evaluation of Pumping Test Data. Figure 2.3: Reservoir limit testing for pressure drawdown data. Ground Water Assessment Development and Management. Transactions, American Geophysical Union, 27(2): 198–205. A generalized graphical method for evaluating formation constants and summarizing well field history.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
